< Back | Home | Edit page | 🙋 Check for open issues |
Data Flow Architecture
The Artsdata linked open data ecosystem is divided in three areas:
- Data providers;
- Artsdata knowledge graph;
- Data consumers.
The following figure illustrates how data flows in and out of Artsdata.ca.
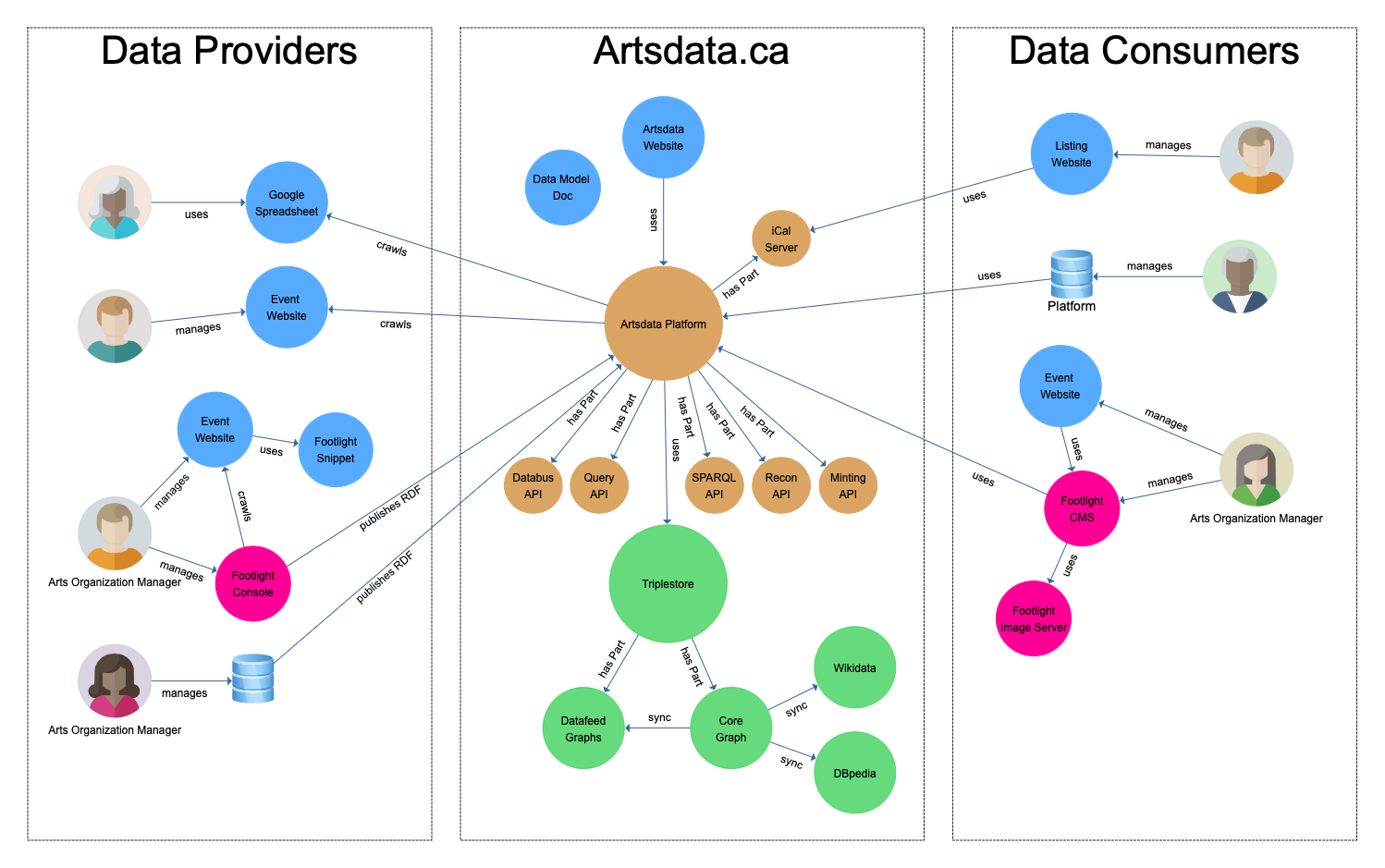
Breakdown of architecture
- Artsdata.ca Website
- Data Consumers
- Artsdata Data Model & Ontology
- Footlight Console
- L'outil Google Sheet-vers-Artsdata
- Google Sheet-to-Artsdata Tool
- Google Sheets
- Databus API
- iCal Server
- Minting API
- Query API
- Reconciliation API
- SPARQL Endpoint & Federation
- Artsdata Triplestore
Detailed presentation of each area
Data providers
For data providers, such as arts organizations (producers, presenters, agents, venues) and artists, a range of Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) processes and tools are available:
- Front-end ETL with JSON-LD scraping (i.e. scanning web pages with the Artsdata crawler, retrieving JSON-LD structured data and copying it);
- Front-end ETL combining JSON-LD scraping and natural language processing;
- ETL via endpoints (APIs, JSON-LD endpoint);
- Google Sheet to Artsdata (a tool to convert spreadsheet information into linked open data);
- Mint from Wikidata (a service to import data previously loaded to Wikidata);
- Footlight Console (event information management software for a single site);
- Footlight CMS (event information management software for multiple sites);
- Artsdata Load API (Graph-store API) that accepts RDF data meeting all Artsdata data modelling requirements and constraints (SHACL defined in Artsdata.ca or ShEx when coming from Wikidata).
Front-end extraction is performed by the Artsdata crawler, a user agent that functions just like the search engines’ robots. Some websites may not allow or may restrict web page crawling. To find out how to allow the Artsdata crawler, consult the Artsdata-Crawler Permission documentation page.
Prior to being loaded to Artsata, data must meet minimal the requirements Artsdata data model for the entity type. SHACL shapes are used to validate data before importing.
Consult the Data Contributor Conditions page to learn more about the extraction, transformation, loading and semantic enrichment processes.
All data submitted to Artsdata.ca requires a user account registered with artsdata.ca. Third-party developers are welcome and can use the Artsdata Databus API to load data. If you wish to register with Artsdata or if you need assistance to load your data, please contact the Artsdata team.
All data submitted to artsdata.ca is agreed upon by the registered account to be CC0.
For more information, visit the Data Contributor Conditions page.
Artsdata data providers include associations, unions, industry platforms, ticketing services, and individual arts organizations (see the list).
Artsdata knowledge graph (kg.artsdata.ca)
Artsdata aggregates and shares descriptive metadata related to cultural events (and related entities) from/with multiple websites and external databases. Data is published as Linked Open Data with persistent identifiers (i.e. URIs) that can be used to link events to artists, venues and arts organizations.
The Artsdata data model is implemented using classic RDF ontologies. It is a sub-set of Schema.org and maps data to a multitude of other classic (i.e. LRMoo, DBpedia) and non-classic (i.e. Wikidata) ontologies.
Artsdata mints its own Artsdata persistent identifiers (URIs) for named entities when they meet minimal requirements for minting. Registered users can mint an Artsdata URI from a Wikidata URI. Artsdata also uses external URIs (Wikidata, VIAF) for named entities and concepts.
The Artsdata triplestore is a standard (compliant with W3C Standards) RDF triplestore using the “GraphDB Free” product by OntoText.
Data consumers
Data consumers wanting to use the data can access it in a number of ways:
- Browse the knowledge graph interface at kg.artsdata.ca;
- Call the Artsdata Reconciliation API to retrieve persistent identifiers;
- Crawl persistent identifiers to access the associated metadata in JSON-LD format;
- Call the RESTfull Artsdata Query API;
- Subscribe to a custom iCalendar subscription feed via the iCal Server;
- Call the Artsdata SPARQL endpoint.;
- Download a data dump of triples serialized in a variety of formats such as JSON-LD or N-Quads.
The data from Artsdata.ca is CC0 and can be used in other applications without any restrictions.
Artsdata data consumers include listing sites, industry platforms, arts service organizations, destination marketing organizations, government bodies and search engines (see the list). For an overview of use cases, check our user stories.

